Radiofrequency shielding (RF) prevents radiofrequency electromagnetic impulses that create radio frequency interference (RFI). RF shielding involves surrounding possible sources and victims of an electromagnetic field, cable lines, and electronic device circuits with barriers built of conductive and magnetic materials to isolate them from their surroundings. Read More…
Sealing Devices is a leading North American distributor and fabricator of EMI shielding products, including conductive elastomers, Soft-Shield® low closure force gasketing, windows, conductive adhesives, formed-in-place parts, vents and elastomers.
We are one of the first in EMI technologies! Our roots trace back as early as the 1930s. We work hard to bring you the latest and greatest in EMI technologies and distribution. ADIT Electron Tubes manufactures low-level light detection systems and devices. Our photomultipliers are apart of a major international industry that we are a supplier of. Call us today for more information about our EMI...
FMS has been eliminating electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI) issues in commercial & industrial buildings, medical facilities, and research laboratories for over 25 years. Using the latest technology, backed by independent research and development, FMS delivers customized, innovative mitigation solutions for the most complex interference problems worldwide.
More RF Shielding Companies

Radio Frequency interference can impair a device's electrical circuits from operating normally. The characteristics of the shielding material, the design, thickness, the electromagnetic frequency, and the magnitude of any discontinuities on the shield all affect how well RF shielding reduces interference.
Different devices respond differently to radio frequency interference. Communication and electronic devices may operate worse as a result of radio frequency interference. Radiofrequency interference is a common problem in electronics and is not fixed in the actual world. Electrical circuits can both emit and also be susceptible to radiofrequency electromagnetic impulses. The use of RF shielding protects equipment from the negative effects of RF interference.
Materials for RF Shielding
The ability to reflect or block the electrical component of electromagnetic waves is made possible by a material's high conductivity. Therefore, the frequency of the electromagnetic wave, the geometry of the shield, and the material's conductivity and magnetic permeability all affect how successful the shielding is. For example, a material with a high magnetic permeability can provide low reluctance lines of magnetic flux, which is useful for absorbing and pulling magnetic fluxes around the shielding region. Some of the materials that are commonly used include:
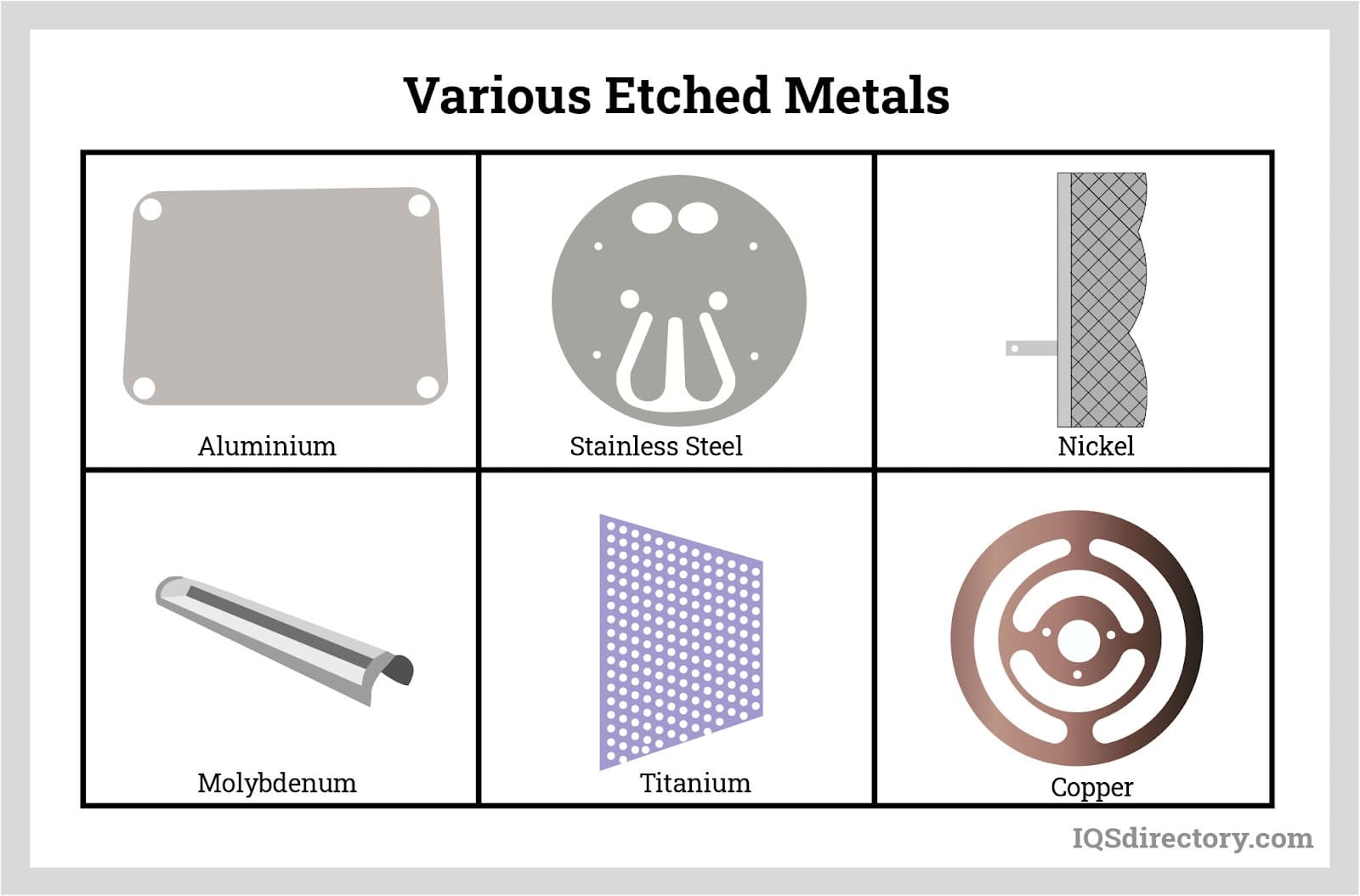
Steel
In contrast to copper alloys and aluminum, steel and other ferromagnetic materials offer low-frequency magnetic field shielding. Depending on the type of steel, they have a variety of RF shielding plus mechanical qualities. Low-carbon steels have increased permeability and saturation points compared to high-carbon steels. The saturation point is the magnetic flux density a material can hold at a particular thickness.
Copper
Due to its superior ability to attenuate and absorb electromagnetic waves' magnetic and electric components, copper is the most reliable material for RF shielding. In addition, it is electrically very conductible. Since copper is simple to produce and can be shaped into a wide variety of desired shapes, copper-based shields can be relatively easily attached as radiofrequency shields to electronic devices. In addition to these properties, copper is resistant to oxidation brought on by the environment and is naturally resistant to corrosion.
Nickel Silver
In very corrosive settings, nickel silver, also known as copper alloy 770, is frequently utilized as a radiofrequency shielding material because it comprises various proportions of nickel, copper, and zinc. It works well for attenuating RFI in the mid-kHz to GHz frequency range. In addition, they are perfect for building RF shielding for MRI equipment, which is prohibited from using magnetic waves because they have a permeability of 1.

Conductive Fabrics
Some conductive fabrics are lightweight textiles coated or combined with metals, including nickel, copper, silver, gold, and carbon. Polyester, silk, cotton, and nylon fibers create conductive fabrics. These materials reduce RFI in confined rooms and spaces and have strong shielding efficiency.

Aluminum
Thin aluminum sheets block low-frequency radio waves. Electronic equipment enclosures can be made of aluminum to provide built-in RF protection. However, aluminum has a conductivity of between 50 and 60 percent less than copper. Hence aluminum RF shielding needs to be thicker to be as effective at shielding as copper.

Types of RF Interference
Electromagnetic waves are made up of opposing electromagnetic and electric waves that oscillate. The wavelength and frequency of electromagnetic waves are used to describe them. The electromagnetic spectrum serves as a representation of these waves' continuity.
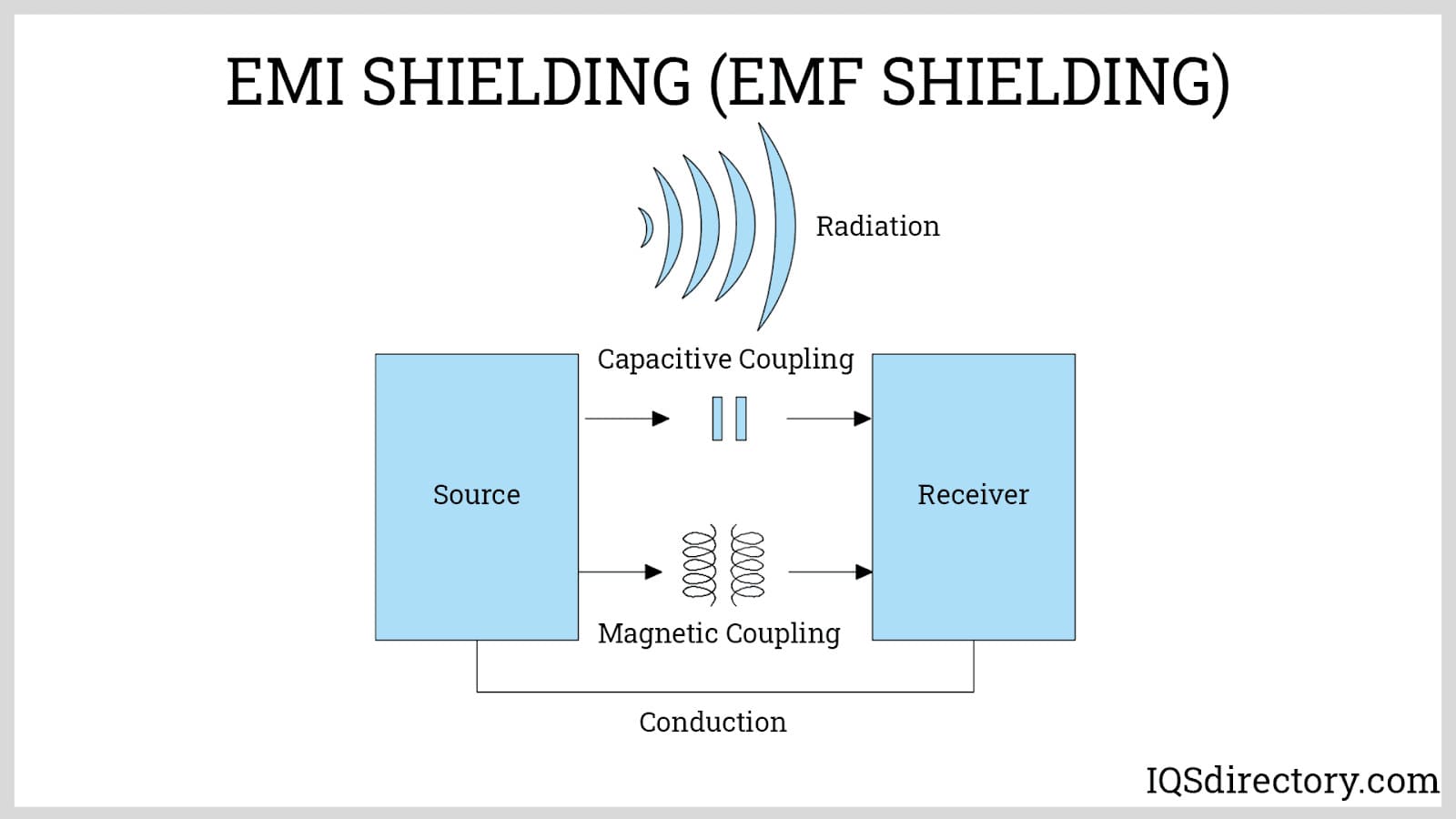
Electromagnetic interference occurs when undesired electromagnetic waves or impulses interfere with an electrical device's ability to work properly. It is frequently referred to as noise or electromagnetic noise. It is possible to categorize radiofrequency interference based on its duration, source, and bandwidth.
Source
Artificial sources of electromagnetic radiation, which can impact nearby equipment and gadgets, are emitted by electronic and electrical devices. The unnatural causes of RFI are divided into intentional and unintentional sources.
Natural Sources
Astronomical events like solar flares, lightning strikes, static electricity, dust storms, cosmic noise, and snowstorms cause RFI to occur naturally.
Duration
Continuous radiofrequency interference (RFI) describes the RFIs that a source constantly emits by radiation or conduction. In contrast, radiofrequency impulse interference happens suddenly or for a very brief period. Impulse RFI frequently upsets the voltage and current balance of linked neighboring devices due to switches and illumination. Both types can be produced from natural or artificial sources.
Bandwidth
Bandwidth is the frequency range in which the RFI is present.
Broadband
There is no single, discrete signal where the interference manifests itself. A natural or artificial source might cause several types of broadband RFI. The sun, which obstructs useful satellite signals from communication equipment, is a naturally occurring cause of this interference.
- Radiative coupling
- Magnetic coupling
- Conductive coupling
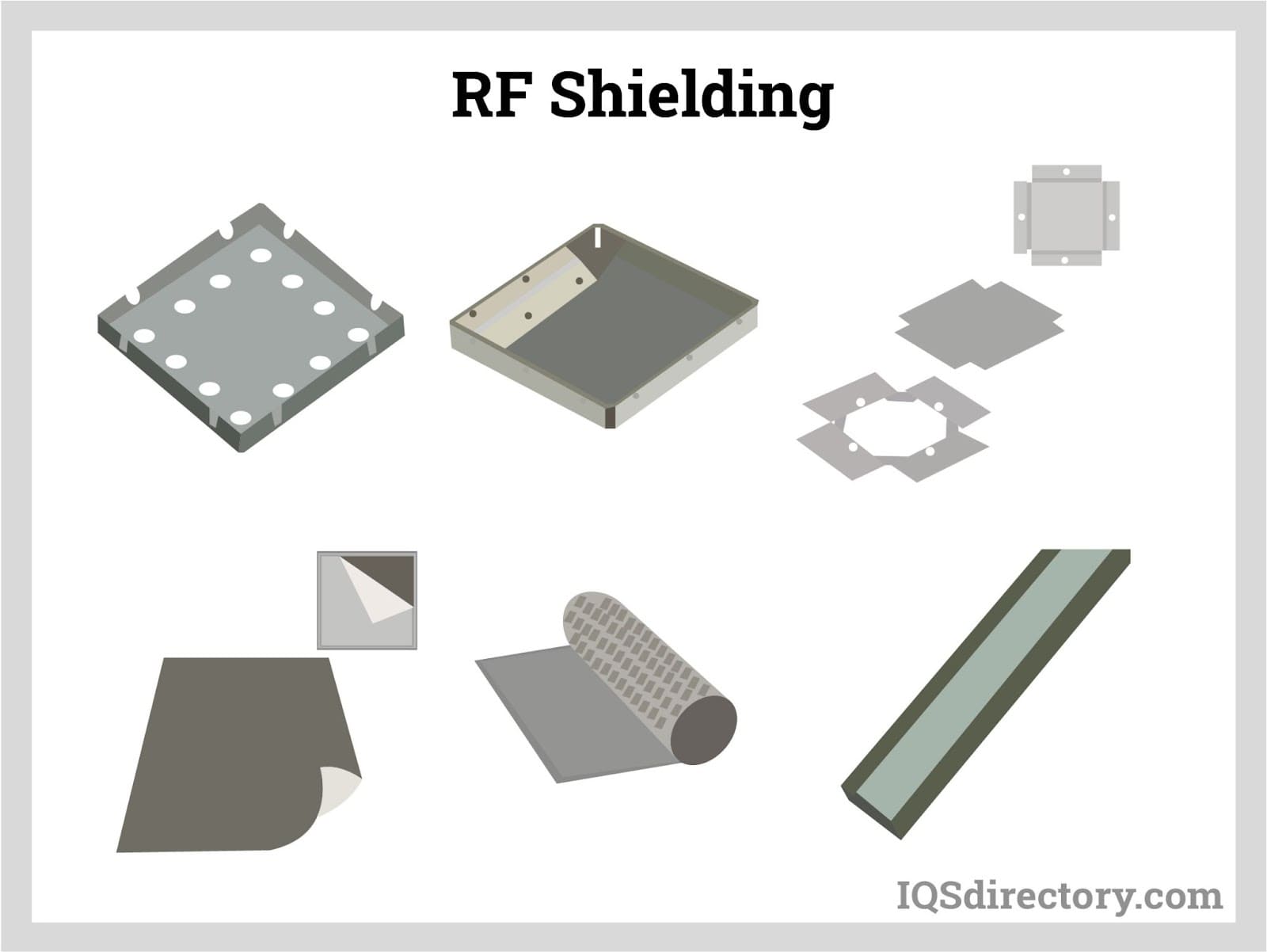
Forms of RF Shielding
Some of the typical RF shielding methods are:
- Cable shielding
- Shielded vents
- Gaskets
- Board-level shielding
- RF-shielded facilities
- Solid enclosures
- Wire mesh and screens
- O-rings
Choosing the Correct RF Shielding Supplier
For the most positive outcome when purchasing RF shielding from a RF shielding supplier, it is important to compare several companies using our directory of RF shielding suppliers. Each RF shielding supplier has a business profile page highlighting their areas of experience and capabilities, along with a contact form to directly communicate with the supplier for more information or request a quote. Review each RF shielding business website using our proprietary website to quickly learn what each company specializes in. Then, use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple RF shielding companies with the same form.





 Electric Coils
Electric Coils Electric Switches
Electric Switches Electric Transformers
Electric Transformers Electronic Connectors
Electronic Connectors Electronic Enclosures
Electronic Enclosures EMI Shielding
EMI Shielding Membrane Switches
Membrane Switches Power Cords
Power Cords Static Eliminators
Static Eliminators Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services